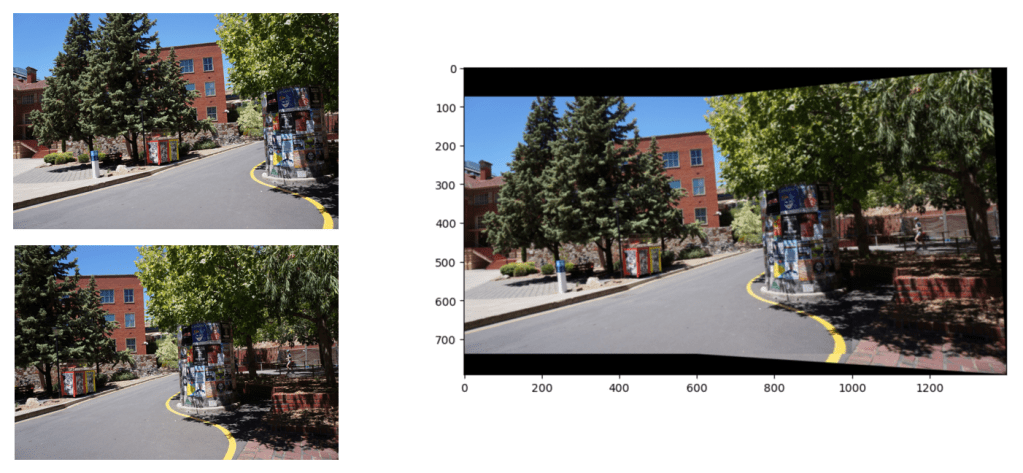
In this project, I implemented a feature-based panorama stitching pipeline, leveraging Harris corner detection, SIFT descriptors, and homography estimation with RANSAC. While OpenCV’s warpPerspective() is used to apply the transformation, the pipeline manually handles feature matching, homography computation, and image blending to create a seamless panoramic image.
To align and stitch images, we first detect and match key points between two overlapping images:
1. Harris Corner Detector:
• Identifies strong corner-like features in both images.
• Uses non-maximum suppression to retain the most distinctive points.
2. SIFT Descriptor Extraction:
• Computes gradient-based descriptors at each key point.
• Converts local gradient orientations into 128-dimensional vectors.
• Ensures robustness against scale and rotation variations.
3. Feature Matching using the Ratio Test:
• Computes Euclidean distances between descriptor vectors.
• Uses Lowe’s Ratio Test to filter out ambiguous matches.
• Retains only high-confidence matches.
Computing the Homography Matrix
With the matched key points, we compute the homography matrix H, which maps one image’s perspective to the other’s:
• RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus) is used to filter out outliers and compute a robust transformation.
• OpenCV’s findHomography() estimates the best H given the matched points.
Once the homography is determined, we warp one image to align with the other:
1. Transform Image B’s Corners:
• The four corners of image B are projected using H .
• This determines the bounding box for the stitched panorama.
2. Warp Image B into Image A’s Coordinate System:
• warpPerspective() is used to apply the homography transformation.
• This aligns image B with image A while preserving geometric correctness.
3. Merging the Images:
• The two images are placed into a single canvas.
• Image A is overlaid directly into the result, filling the appropriate region.
By detecting keypoints, computing homography, and applying perspective warping, this project demonstrates a fundamental pipeline for panorama stitching. While warpPerspective() is used for transformation, the key steps—including feature detection, matching, and blending—are all manually handled, providing insight into how panoramic image alignment works beyond built-in stitching functions.
Below are some more examples of panorama stitching.


Leave a comment